Airflow patterns in aircraft affect a significant number of travellers every year, and the close proximity of passengers in aircraft cabins leaves them vulnerable to disease transmission and infection if the correct ventilation systems are not put in place.
In a study written by one of our customers at Kansas State University, a mock-up Boeing 767 cabin was built and used to study the effects of passenger loading where a number of tests were conducted. The article focuses on 2 scenarios of commercial air travel; the effect of passenger density on the transport of contaminants throughout the aircraft cabin, and the transmission of contaminants throughout the aircraft cabin when the supply is eliminated.
In the first scenario a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO2) and helium (He) is injected as a tracer gas at a seat location in the cabin, and the gas concentration is then sampled at various locations throughout the cabin. This testing is completed with thermal manikins occupying all 77 seats in the mock-up cabin and then repeated with only 38 of the seats (approximately half) occupied. After both passenger loads are tested, the changes in tracer gas concentrations are examined.
In the second scenario the mock-up cabin was brought back to normal operating conditions, then turning off the supply air stream and injecting and sampling tracer gas throughout the cabin, and comparing the tracer concentrations sampled at different locations.
The results of this research show that the loading of passengers inside the aircraft cabin can have a significant impact on the dispersion of tracer gas and airflow patterns throughout the cabin.
Read the full article on airflow patterns by following the link.
The Gascard NG for Airflow Patterns
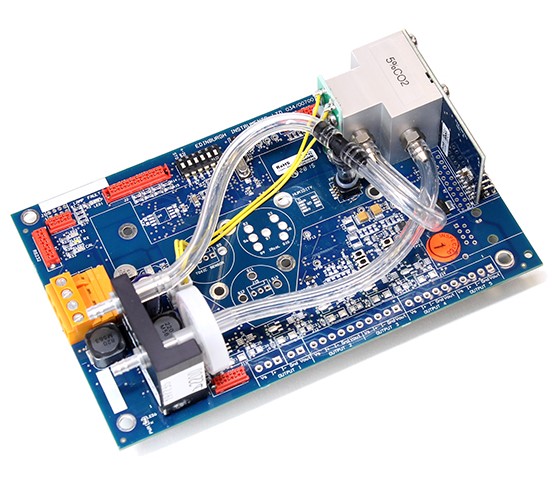 Infrared CO2 analysers were used to sample tracer gas, and were placed in 3 different locations of the mock-up cabin. The first was made using our Gascard NG, and was placed on the roof of the enclosure and sampled the supply air at the inlet of the enclosure.
Infrared CO2 analysers were used to sample tracer gas, and were placed in 3 different locations of the mock-up cabin. The first was made using our Gascard NG, and was placed on the roof of the enclosure and sampled the supply air at the inlet of the enclosure.
The Gascard NG infrared gas sensor is designed for ease of integration with a wide range of gas detection systems that require high quality, accurate and reliable measurement of CO, CO₂, and CH₄ gas concentrations.
For more information on the Gascard NG or our other gas detection solutions, contact a member of our team at sales@edinst.com.
Stay in Touch
If you have enjoyed reading about how our Gascard NG is used for airflow patterns and want to be the first to see all the latest news and product information from Edinburgh Sensors, then sign-up to our infrequent newsletter via the sign-up button below, and follow us on social media.

