What is methane?
Methane (CH4 ) is a colourless and odourless greenhouse gas which is extremely volatile and is one of the major contributors to global warming due to its high potency. Roughly one third of methane gas emissions occur naturally through sources such as wetlands. However, two thirds of emissions are due to human activity, with agricultural activities being a major contributor, particularly from livestock.
Methane and agriculture
Cows, specifically, are responsible for around 40% of the worldwide methane gas emissions. Not only is methane gas a major contributor to global warming, but its volatile nature also presents a health and safety risk within agricultural settings.
Importance of methane gas detection in agriculture
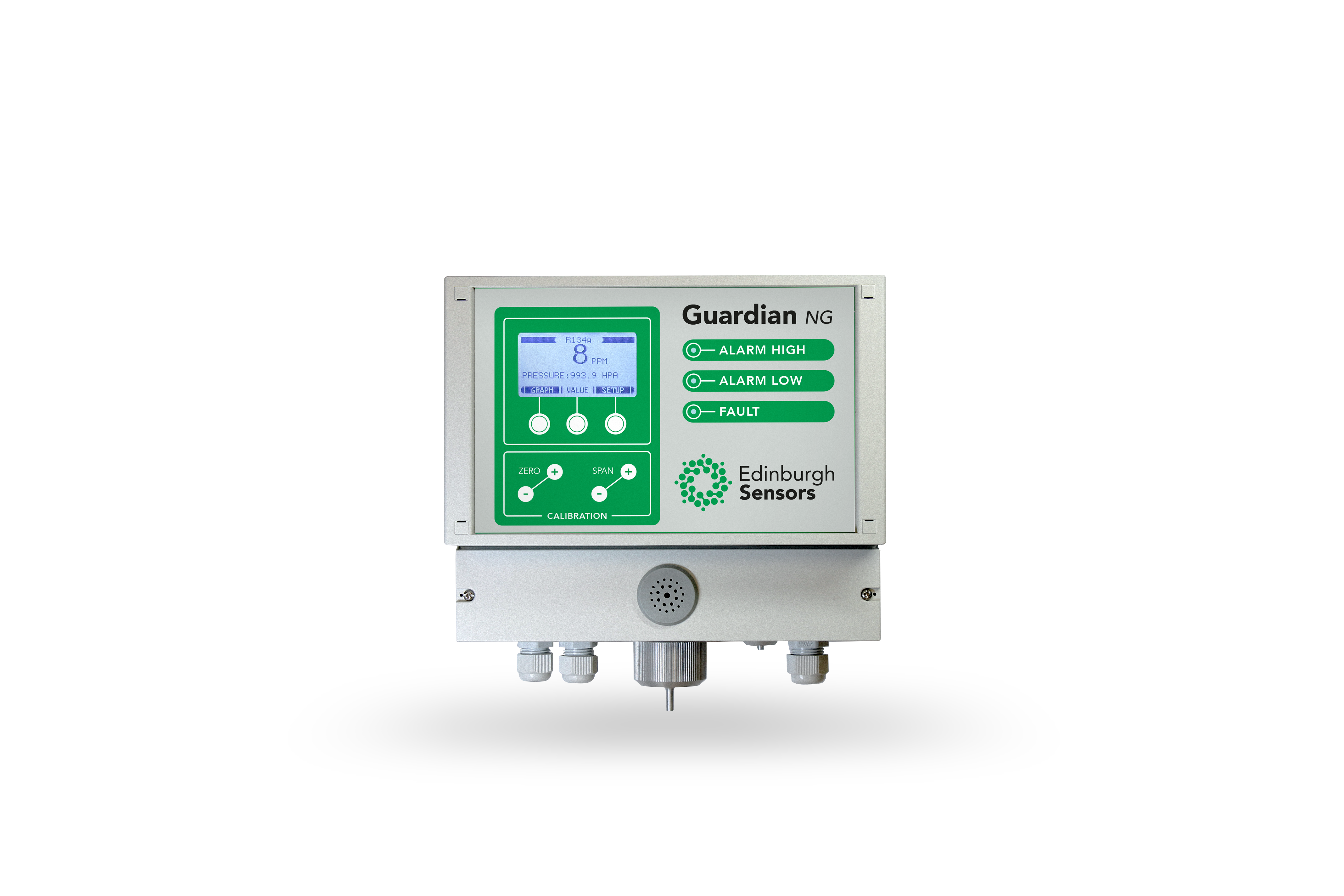
Overall, all vital research into mitigating agricultural methane relies on monitoring methane gas production by cows accurately. The change in methane emission could be small, therefore sensing technologies which are sensitive as well as accurate are vital. An effective solution for this is NDIR sensing technology, as methane highly absorbs infra-red light. The Sensors Guardian NG is a type of NDIR device and is the ideal solution for precise methane monitoring within agricultural research and operations.

How do we reduce methane gas emissions:
Reducing methane emissions is essential for both the health and safety of the planet and the people in it. Since methane is extremely volatile, it poses a major health risk to us, and so monitoring methane emissions is essential, particularly for industries where methane is a byproduct, like livestock farming.
- Monitor emissions
The first step to reducing methane emissions from agricultural sources is to measure current gas emissions, so that we can make well-informed decisions and work towards monitoring and reducing emissions. The perfect solution for monitoring gas levels is the Sensors Guardian NG. Featuring a rapid response time, and accurate readings, even when the change in emissions is minor, it’s crucial for understanding baseline agricultural methane output.
- Explore approaches to reduce emissions
A major contributor to methane emissions is the agriculture industry. Cows produce large amounts of methane when they defecate or burp, and this methane is released into the atmosphere. Roughly 40% of global methane emissions are caused by cows alone, and so finding a way to reduce these emissions is vital. This includes exploring new feed additives, breeding strategies, and manure management techniques to lower the methane footprint of livestock.

