The anaerobic digestion process is typically used as a means of waste disposal or energy production. Anaerobic digestion of bio-waste in developing countries is extremely beneficial as it doesn’t just generate clean and safe energy, it also contributes towards other economic development issues and has considerable environmental benefits.
In this article we will explore the many benefits of the anaerobic digestion process for developing countries, and the vital role of Edinburgh Sensor’s carbon dioxide and methane gas sensors in the process.
What is The Anaerobic Digestion Process?
Anaerobic digestion is a microbiological process whereby organic matter, such as animal manure, is decomposed in the absence of oxygen. The process occurs naturally in environments such as swamps, or an engineered approach can be used to process organic biodegradable matter in airproof reactor tanks which produces combustible methane gas, known as biogas.
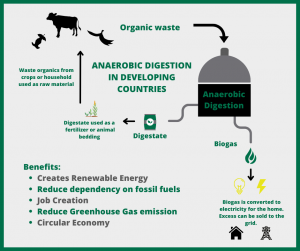
What are The Benefits of The Anaerobic Digestion Process?
There is a long list of benefits of the anaerobic digestion process of organic waste. These include the generation of renewable energy, a reduced dependency on fossil fuels, job creation, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and the closing of the nutrient cycle.
Not only does the anaerobic digestion process transform organic waste material into valuable resources, but it also reduces solid waste and disposal costs. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy contributes towards the preservation of natural resources, the decreased use of fossil fuels and the reduction of pollution.
What are The Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion of Bio-Waste in Developing Countries?
The anaerobic digestion process has now become widespread in many developing countries across the world, especially throughout Asia, where 40 million systems were installed in China in 2011, and a further 4 million in India. It is currently less prevalent in Africa and South America, however multiple support projects have recently been implemented to make a change to this.
The 3 key development drivers for introducing the anaerobic digestion process include providing locals with biogas fuel as a cost-efficient household energy source, improving soil fertility, and reducing consumption of fossil fuels and respective pollution and deforestation.
1. Production of Cost-Efficient Household Energy
One of the reasons why home biogas plants can benefit those in developing countries is because the technology is an energy source that is is simple and economical to set up, and possible for both small and large scale production. Using the anaerobic digestion process, a household with just three cattle or seven pigs can generate sufficient gas to meet their basic domestic energy needs, including cooking and lighting.
As shown in the image below, a household biogas plant requires a 6 cubic meter pit lined with concrete and an air-tight concrete cover. Animal dung and water must be placed into a concrete mixing bowl, and a metal crank blends it together and pushes it into the underground pit through a pipe. Deprived of oxygen, this waste mix decomposes and gives off methane, which flows into a narrow pipe leading to the kitchen where it can be used as fuel.
Considerable economic benefits can arise for those in developing countries from the sale of electricity and savings made by not having to buy standard energy for household consumption.

Image source: https://www.nytimes.com/2011/10/26/business/energy-environment/biogas-offers-poor-countrys-a-cleaner-safer-fuel.html
2. The Improvement of Soil Fertility
The residue of the anaerobic digestion process, bio-slurry, benefits farmers in developing countries because it can be used as a potent organic fertiliser to enhance agricultural productivity and sustain soil fertility.
Research has confirmed that the increased nutrient supply from organic materials, which includes digestate and compost, provides higher crop yields which can be of equal quality to crops grown with bagged fertilisers. This is because the bio-slurry provides a nutrient benefit, improves soil structure and reduces a need for manufactured fertiliser, which consequently reduces costs and improves overall value of farmland. This economic return can be hugely beneficial for rural development.

3. Environmental Benefits
There are clear environmental benefits to using biogas, for both forest conservation, pollution reduction, and combating climate change.
The capturing and use of biogas is powerful in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, which are the key contributor to global warming. Greenhouse gases are reduced in two ways; firstly, the biogas produced is a source of renewable energy which can be used instead of fossil fuels. Secondly, the capturing of biogas during the anaerobic digestion process reduces the presence of methane in the atmosphere, which is 21 times more harmful than carbon dioxide, and therefore reduces pollution and slows the effects of global warming.
Further environmental benefits arise from the reduction of deforestation as biogas provides a source of energy that would otherwise be provided by wood fuel and require trees to be cut down. An average home biogas system can reduce firewood use by about 4.5 tons each year, which translates into 4 tons of greenhouse gas emissions, according to the World Wildlife Fund.

How does The Anaerobic Digestion Process Require Gas Sensing?
Gas sensing is vital for the production of biogas, because early gas detection through carbon dioxide and methane sensing is crucial to the evaluation of the efficiency of the Anaerobic Digestion process.
Gas concentration levels that are either too high or too low can indicate a change in the efficiency of the fermentation process. Anaerobic process control systems measure the methane content (and often the carbon dioxide content) of the gas stream to control or evaluate the anaerobic digestion process and warn of any potential problems.
Edinburgh Sensors provide high performance OEM gas detectors that are able to give fast, accurate and reliable measurements of both carbon dioxide and methane concentrations during the anaerobic digestion process.
If you are interested in the specific applications of gas sensing for biogas production and would like to find out more, why not have a read of our relevant articles:
- Carbon Dioxide and Methane Sensing for Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas Applications.
- Anaerobic Digestion of Slaughterhouse Wastes after Thermal Treatment using ADM1.
- Using Anaerobic Biomass Digestion to Produce Hydrogen and Biofuel.
Which Edinburgh Sensors Products are suitable for The Anaerobic Digestion Process?
The Gascard NG is Edinburgh Sensor’s OEM sensing solution for measuring either Methane (CH₄) or Carbon Dioxide (CO₂). It has been designed for easy integration by system integrators and is able to measure 0-100% or 0-30% of CO and 0-30% of CO₂. The sensor features on board Barometric Pressure Correction, and extensive Temperature compensation.
In an addition to OEM Gas sensors, Edinburgh Sensors have been providing gas monitors based upon our proprietary infrared sensor technology for many years. The Guardian NG Gas Monitor is wall-mounted, in an IP54 enclosure, with an integral power supply and sample pump, allowing samples to be taken remotely from over 30 meters away. This Gas Monitor can measure 0-100% of Carbon Monoxide (CO) or 0-30% of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂).


Get in Touch for More Information about Gas Sensing and the Anaerobic Digestion Process
If you have enjoyed learning about the benefits of the anaerobic digestion of bio-waste in developing countries, and would like to find out more about how Edinburgh Sensors can assist your anaerobic digestion process, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with a member of our team.
Why not sign up to our infrequent eNewsletter via the link below and join us on social media to stay up to date with the latest news, products and research from Edinburgh Sensors.

