Despite the many similarities, there are also many differences between carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. They are often understandably mistaken as the same gas, however, the distinction between them is crucial when it comes to gas sensing.
What Is Carbon Dioxide?
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) is a chemical compound consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. It is a colourless and odourless gas at room temperature and is present in the Earth’s atmosphere at a low concentration. CO₂ enters the atmosphere through the respiration of organisms, the decomposition of organic matter, the burning of fossil fuels and fermentation. It is taken in by plants through the process of photosynthesis and can be harmful to the environment as it is a greenhouse gas which traps heat energy within the earth’s atmosphere and contributes towards global warming. Some of the main uses of CO₂ include freezing food, carbonating beverages, extinguishing fires, and various uses in agricultural and medical applications.
Find out more about what carbon dioxide is and what carbon dioxide is used for.
What Is Carbon Dioxide Used For?

Uses Of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon Dioxide is used for a number of applications in different industries, including HVAC, landfill, horticulture, controlled atmosphere storage and packaging, metal heat treatments, TOC and many more. Each of these applications would not be possible without precise CO₂ measurement. If you are interested in finding out more about specific uses of carbon dioxide and CO2 sensing, why not have a browse of the following articles…
- The Use of a Carbon Dioxide Sensor in the Conservation and Ripening of Fruits
- The Role of Carbon Dioxide Measurement in the Prevention of Sick Building Syndrome
- The Role of Carbon Dioxide Measurement in Wine Production
- Nuclear Applications using a Carbon Dioxide Sensor
- Carbon Dioxide Measurement for the Early Detection of Spoilage in stored grains
- Monitoring CO2 Concentrations in Pig and Poultry Processing
What Is CO Carbon Monoxide?
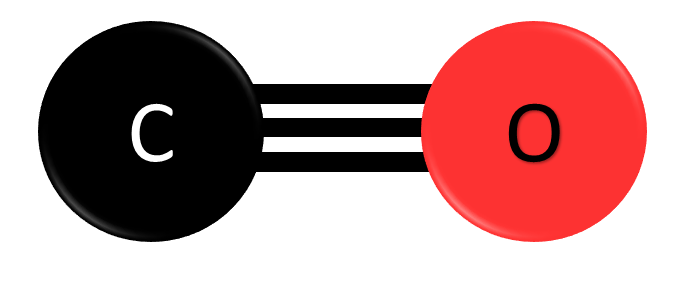
Carbon Monoxide (CO) is a chemical compound which contains one carbon atom and one oxygen atom and is also a colourless and odourless gas. Unlike CO₂, it is entirely human-made and is not naturally present in the atmosphere. It is produced during the incomplete burning of organic matter, which can occur from motor vehicles, heaters, or cooking equipment that run on carbon-based fuels. CO is therefore spatially variable and short lived in the atmosphere, where it has a role in forming ozone at a ground level. When carbon monoxide is present in concentrations greater than 35 ppm it is toxic to humans and animals, as it prevents the blood from carrying oxygen.
Find out more about carbon monoxide.
Uses Of Carbon Monoxide
Carbon Monoxide sensing using a CO sensor is equally important because detection cannot be done by vision or smell alone. It is necessary because it can prevent carbon monoxide poisoning which can cause loss of consciousness, seizures of even deaths. Furthermore, CO sensing takes place across a number of other applications, which you can read about by following the links below.
- Carbon Monoxide detection for Gasification
- Endothermic Process and Heat Treatment Furnaces
- Process Control
- HVAC
Carbon Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide Sensing – What’s The Difference?
The detection of the two gases differ because CO₂ detectors commonly use infrared sensors, while CO identification uses electrochemical sensors. However, CO can also be detected using NDIR sensing.
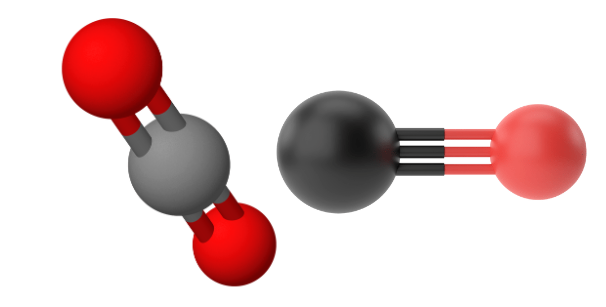
Despite the fact that CO₂ and CO is difficult to detect, Edinburgh Sensors’ range of sensors allow the gas to be strongly absorbed using non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) technology. NDIR sensors offer highly sensitive CO₂ detection because the gas can absorb infrared light very strongly and has characteristic fingerprint signals for unambiguous identification so even trace amounts of gas can be detected. Find out more about non-dispersive infrared gas detection here.
Edinburgh Sensors’ CO and CO₂ Detectors
At Edinburgh Sensors, we are the market leaders with over forty years’ experience developing highly sensitive, rapid response near-infrared sensors for detection of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
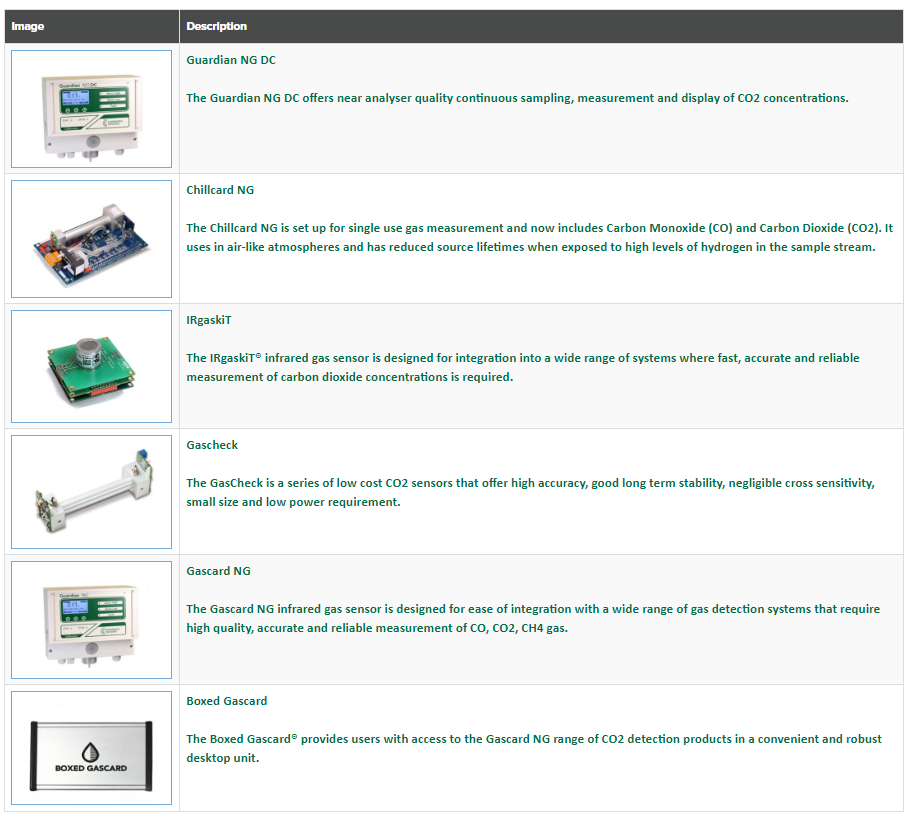
Depending on the exact needs, Edinburgh Sensors offers a range of sensors for CO₂ / CO measurement, including the Gascard NG, Chillgard NG, Guardian NG, Boxed Gascard, IRgaskiT, and Gascheck. Of these, the Gascard NG offers a huge amount of flexibility in its set-up, monitoring options and integration into connected systems.
Follow the links below to find out more about each of these sensors.
Let Us Help With Your Carbon Dioxide or Carbon Monoxide Detection…
If you have enjoyed this article about the difference between Carbon Dioxide and Monoxide Sensing and would like to find out more, please get in touch, we look forward to assisting you.
Or if you would like to stay updated with future news and research from the gas sensing world, why not join us on social media and sign up to our infrequent newsletter by clicking the link below.

